Are you perpetually battling colds and flu, wondering if there's a secret weapon to fortify your body's defenses? The answer might lie in something as simple as optimizing your vitamin D levels a critical component in maintaining a robust immune system.
Vitamin D, often dubbed the "sunshine vitamin," has long been recognized for its role in bone health. However, emerging research underscores its profound impact on the immune system. From modulating immune cell function to reducing susceptibility to autoimmune diseases, vitamin D is proving to be a pivotal player in overall health. But what does the science actually say about vitamin D and its effects on immunity? Let's delve into the details, exploring the intricate relationship between this essential nutrient and the body's ability to fight off illness.
| Category | Information |
|---|---|
| Overview | Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin crucial for bone health and immune function. It's produced in the skin upon exposure to sunlight and can also be obtained through diet and supplements. |
| Mechanism of Action | Vitamin D acts as a hormone, binding to the vitamin D receptor (VDR) present in various cells, including immune cells. This binding regulates gene expression, influencing immune responses. |
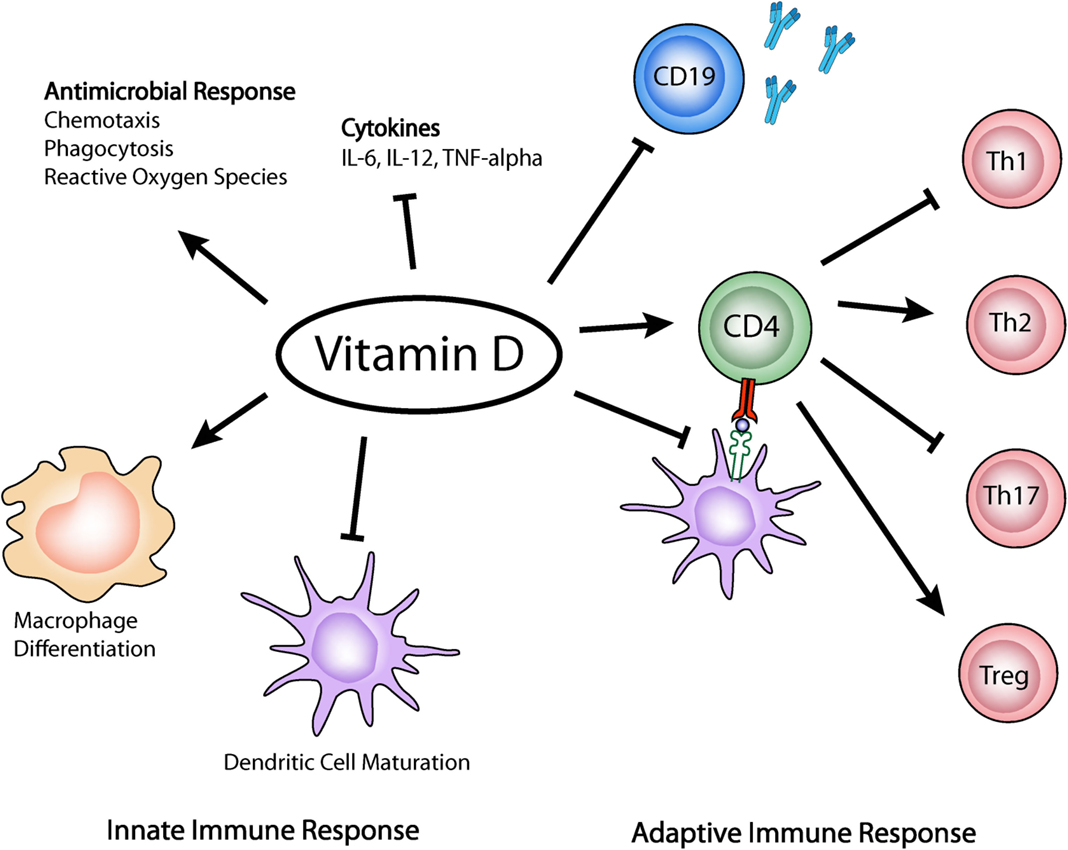
| Role in Innate Immunity | Vitamin D enhances the innate immune response by promoting the production of antimicrobial peptides like cathelicidin, which helps fight off bacterial and viral infections. |
| Role in Adaptive Immunity | Vitamin D modulates the adaptive immune response by influencing the differentiation and function of T cells and B cells, thus preventing excessive inflammation and autoimmunity. |
| Deficiency and Immune Health | Vitamin D deficiency impairs immune function, increasing susceptibility to infections and autoimmune diseases. |
| Supplementation | Vitamin D supplementation can improve immune health, particularly in individuals with low vitamin D levels. The recommended daily intake varies depending on age, health status, and other factors. |
| Research & Studies | Numerous studies have explored the effects of vitamin D on the immune system, demonstrating its role in preventing respiratory infections, autoimmune diseases, and other health conditions. |
| Additional Resources |
|
For now, the bottom line regarding the impact of vitamin D on the immune system is that avoiding severe deficiency enhances immune health and reduces vulnerability to autoimmune conditions. This conclusion stems from a growing body of evidence highlighting vitamin D's role in both adaptive and innate immune responses, suggesting that sufficient vitamin D levels are associated with immune tolerance. Considering the significant function of vitamin D for both adaptive and innate immune responses, its level is intricately linked to immune tolerance. Specifically, vitamin D influences the behavior of immune cells, potentially explaining its beneficial effects against certain autoimmune diseases.
- Filmyfly Safe To Stream Reviews Alternatives More Warning
- Erika Jaynes Son Tommy Zizzo Updates Family Rhobh Secrets
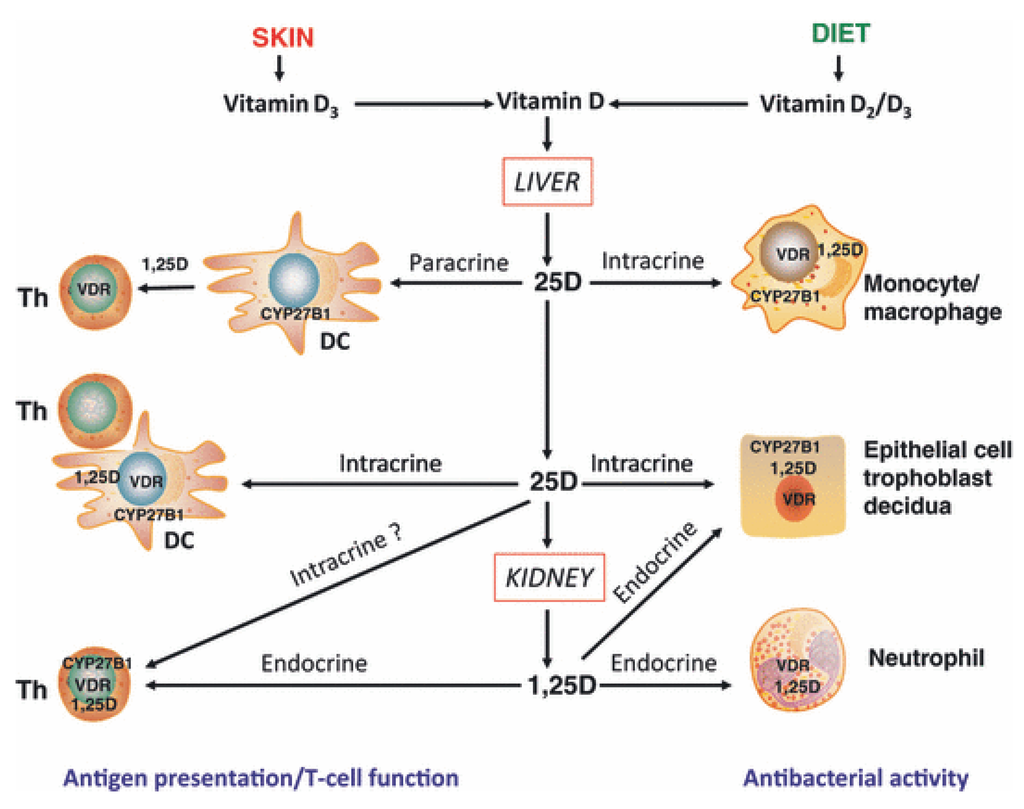
Calcitriol, the active form of vitamin D, functions as a pluripotent regulator within the innate immune system. The process begins when a bacterial infection triggers a series of immune responses, and calcitriol plays a crucial role in modulating these responses to effectively combat the infection. In healthy individuals, T cells, critical components of the adaptive immune system, are also influenced by vitamin D. The airway epithelium and alveolar macrophages, located in the lungs, express the enzyme CYP27B1, which produces the active metabolite of vitamin D, 1,25(OH)2D. These cells also possess the vitamin D receptor (VDR), allowing them to respond directly to vitamin D signaling.
Vitamin D and its metabolites bolster the innate immune response, acting as the first line of defense against viral and bacterial infections while simultaneously restricting excessive inflammation. This dual action is crucial for effectively clearing pathogens without causing undue harm to the body's tissues. Beyond mineral metabolism and skeletal health, vitamin D actively regulates the immune system, solidifying its importance in overall wellness.
Reports suggest an inverse relationship between vitamin D levels and the incidence of infections and autoimmune diseases, further supporting its role in immune regulation. Vitamin D and 1,25(OH)2D3, another active form, are known to modulate the innate immune response. This regulatory function extends to various components of the innate immune system, including macrophages, dendritic cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and innate lymphoid cells (ILCs). As such, vitamin D plays a critical role in the pathophysiology of many diseases.
Given that the lungs and immune system undergo significant development during gestation and continue to mature postnatally, the available data indirectly highlight the importance of vitamin D during these critical stages. Prenatal or postnatal vitamin D insufficiency may have lasting consequences for child health, underscoring the need for adequate vitamin D intake during pregnancy and early childhood.
Some studies suggest that vitamin D can increase serum levels of cathelicidin, an antimicrobial peptide that modulates interferon-gamma (IFN-) activity against tuberculosis. Both IFN- and vitamin D are recognized immune modulators, and their interaction may be particularly relevant in the context of infectious diseases. The increase in IFN- could be attributed to the immune suppression observed in tuberculosis, which may be mitigated by vitamin D supplementation.
Recent literature findings emphasize the link between sunlight exposure, vitamin D, inflammation, and the immune system in both health and disease. Vitamin D is currently a hot topic in research and clinical practice, as well as in everyday life. Over the past decades, scientists have gathered substantial evidence indicating that widespread vitamin D deficiency has negative impacts not only on the skeletal system but also on the development and progression of various diseases.
Another significant finding is the association between vitamin D and a reduction in autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis. This protective effect may stem from vitamin D's ability to boost immune function while simultaneously suppressing excessive inflammation. The intricate balance between these two actions is essential for maintaining immune homeostasis and preventing autoimmune disorders.
Adequate Intake (AI) recommendations for vitamin D vary across countries and professional societies, reflecting ongoing efforts to refine our understanding of its biology and clinical implications. These differences also stem from the varying purposes of the guidelines, whether for public health in a healthy population or for clinical practice in individuals with specific health conditions. A more complete understanding of vitamin D's complex interactions with the immune system is needed to establish definitive guidelines for optimal intake.

Detail Author:
- Name : Ansel Johnston IV
- Username : keebler.alek
- Email : bret88@gmail.com
- Birthdate : 1990-05-12
- Address : 71079 Kunze Avenue Apt. 627 North German, LA 74451
- Phone : +1.640.426.5747
- Company : Schiller, Dickens and O'Kon
- Job : Avionics Technician
- Bio : Aut est amet itaque voluptatem sed non. Cum provident praesentium omnis consectetur expedita illum commodi tempore. Aspernatur itaque nihil est. Minus cumque veniam et non enim exercitationem.
Socials
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/kshlerind
- username : kshlerind
- bio : A porro praesentium quia omnis facilis explicabo consectetur necessitatibus.
- followers : 5550
- following : 2985
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/derekkshlerin
- username : derekkshlerin
- bio : Et ad dolore non voluptatem. Laboriosam itaque tempora est omnis distinctio necessitatibus.
- followers : 2868
- following : 2319
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/derekkshlerin
- username : derekkshlerin
- bio : Ad et nesciunt nemo voluptas vero.
- followers : 6465
- following : 1911