Ever wondered how to bridge the gap between the Celsius you hear on international news and the Fahrenheit you're familiar with? Understanding temperature conversions is more than just a mathematical exercise; it's about connecting with the world and interpreting the environment around you.
When dealing with temperature, it's not just about numbers, its about understanding the implications. A simple conversion can unlock vital information, whether youre baking a cake with a recipe from abroad or assessing the severity of a global heatwave. Let's delve into the specifics, particularly when grappling with a rather toasty 379 degrees Celsius.
Imagine a scenario where you need to understand a scientific report that states a critical process occurs at 379C. To make that temperature meaningful in a Fahrenheit context, you need a reliable conversion. Thankfully, the formula is straightforward.
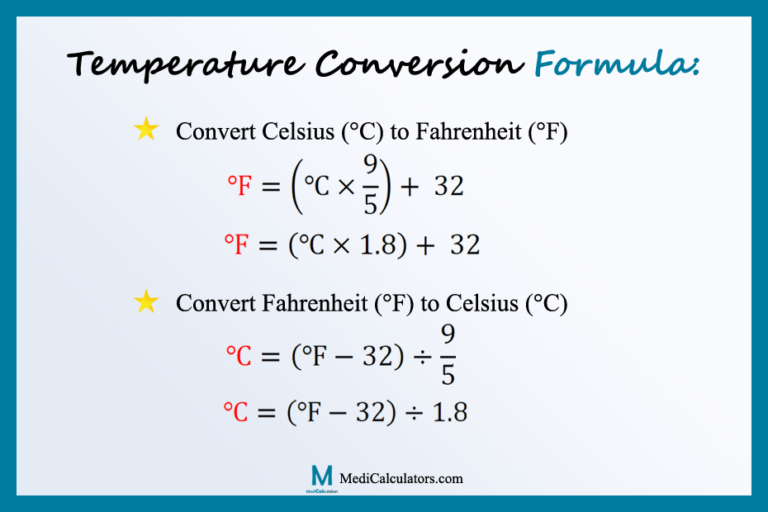
The fundamental equation for converting Celsius (C) to Fahrenheit (F) is given by: [\u00b0F] = [\u00b0C] (9/5) + 32. This formula dictates that you multiply the Celsius temperature by 9/5 (or 1.8) and then add 32 to the result. This calculation provides the equivalent temperature in Fahrenheit.
So, let's apply this to our example of 379C. To convert 379C to F, we substitute 379 into the formula: F = 379 (9/5) + 32 F = 379 1.8 + 32 F = 682.2 + 32 F = 714.2 Therefore, 379 degrees Celsius is equal to 714.2 degrees Fahrenheit.
This conversion reveals that 379C is an extremely high temperature, far beyond typical environmental conditions. It's a temperature more commonly encountered in industrial processes, certain scientific experiments, or specialized equipment. The process of converting Celsius to Fahrenheit involves a simple multiplication and addition, making it accessible to anyone with basic arithmetic skills.
For those who prefer a step-by-step approach, heres how the conversion works: First, multiply the Celsius temperature (379C) by 1.8. This yields 682.2. Then, add 32 to this product. 682.2 + 32 = 714.2. Therefore, the Fahrenheit equivalent of 379C is 714.2F.
It's worth noting that this formula provides a precise conversion. While approximations like multiplying by 2 and adding 30 can give a rough estimate, they lack the accuracy needed for scientific or technical applications. The 9/5 + 32 formula is the gold standard for Celsius to Fahrenheit conversions.
To fully appreciate the significance of temperature scales, consider the context in which they are used. Celsius, also known as centigrade, is the standard in most of the world for everyday temperature measurements. Water freezes at 0C and boils at 100C, providing easy reference points. Fahrenheit, on the other hand, is primarily used in the United States. In the Fahrenheit scale, water freezes at 32F and boils at 212F.
Understanding the differences between these scales is essential for international communication, especially in fields like science, engineering, and meteorology. A misinterpretation of temperature could lead to significant errors or misunderstandings. The formula (c 9/5) + 32 = f is the bedrock of accurate Celsius to Fahrenheit conversions.
Furthermore, many online tools and converters are available to simplify this process. These converters eliminate the need for manual calculations, reducing the risk of human error. They are particularly useful for quick and frequent conversions. However, it's always beneficial to understand the underlying formula to grasp the relationship between the two temperature scales.
Let's consider another practical example. Suppose you're following a European recipe that specifies an oven temperature of 200C. To convert this to Fahrenheit, you apply the formula: F = 200 (9/5) + 32 F = 200 1.8 + 32 F = 360 + 32 F = 392 Therefore, an oven temperature of 200C is equivalent to 392F. This conversion ensures you set your oven to the correct temperature for optimal cooking results.
But what if you need to go the other way and convert from Fahrenheit to Celsius? The formula for this conversion is: C = (F - 32) (5/9). This formula subtracts 32 from the Fahrenheit temperature and then multiplies the result by 5/9. This gives you the equivalent temperature in Celsius.
For instance, let's convert 68F to Celsius: C = (68 - 32) (5/9) C = 36 (5/9) C = 20 Therefore, 68 degrees Fahrenheit is equal to 20 degrees Celsius. This is a common room temperature, illustrating the practical application of the Fahrenheit to Celsius conversion.
Understanding temperature conversions is also crucial in scientific research. Many experiments require precise temperature control, and data may be reported in either Celsius or Fahrenheit. Researchers must be able to convert between these scales accurately to ensure the validity and reproducibility of their results. A minor error in temperature conversion could compromise an entire experiment.
Moreover, in the field of meteorology, temperature plays a critical role in weather forecasting. Weather reports often provide temperatures in both Celsius and Fahrenheit to cater to different audiences. Understanding these temperatures allows people to make informed decisions about clothing, outdoor activities, and safety precautions.
Consider the situation where a weather report indicates a high of 30C. To convert this to Fahrenheit: F = 30 (9/5) + 32 F = 30 1.8 + 32 F = 54 + 32 F = 86 Therefore, a high of 30C is equivalent to 86F. This conversion helps individuals in the United States better understand the expected weather conditions.
In addition to Celsius and Fahrenheit, the Kelvin scale is another important temperature scale, particularly in scientific contexts. Kelvin is an absolute temperature scale, meaning that 0 Kelvin is the absolute zero point, where all molecular motion ceases. The relationship between Celsius and Kelvin is straightforward: K = C + 273.15 To convert from Celsius to Kelvin, simply add 273.15 to the Celsius temperature.
For example, to convert 25C to Kelvin: K = 25 + 273.15 K = 298.15 Therefore, 25 degrees Celsius is equal to 298.15 Kelvin. This conversion is often used in thermodynamics and other branches of physics.
The formula for converting Fahrenheit to Kelvin is a bit more complex, requiring two steps. First, convert Fahrenheit to Celsius using the formula: C = (F - 32) (5/9) Then, convert Celsius to Kelvin using the formula: K = C + 273.15 By combining these two formulas, you can convert directly from Fahrenheit to Kelvin.
Suppose you want to convert 77F to Kelvin. First, convert to Celsius: C = (77 - 32) (5/9) C = 45 (5/9) C = 25 Then, convert to Kelvin: K = 25 + 273.15 K = 298.15 Therefore, 77 degrees Fahrenheit is equal to 298.15 Kelvin.
The importance of accurate temperature conversions cannot be overstated. Whether you're a scientist, engineer, cook, or simply someone who wants to understand weather reports, knowing how to convert between Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin is a valuable skill. The formulas may seem simple, but their applications are vast and far-reaching. From controlling industrial processes to understanding global climate change, temperature conversions play a crucial role in our understanding of the world around us. Remember to always double-check your calculations and use reliable conversion tools to ensure accuracy. The temperature is out there, waiting to be understood, one conversion at a time.
Consider a scenario where an industrial furnace operates at 379C. It's crucial to understand this temperature in Fahrenheit for safety protocols, equipment calibration, and material selection. A precise conversion helps engineers make informed decisions to prevent accidents and ensure optimal performance.
In the realm of baking and cooking, precise temperature control is paramount. Many recipes, especially those from different countries, use Celsius. Converting these temperatures to Fahrenheit ensures that the oven is set correctly, preventing undercooking or burning the food. This is especially important for delicate pastries and souffls.
Furthermore, in the medical field, temperature conversions are essential for monitoring patient health. Body temperature is a critical indicator of illness, and healthcare professionals must be able to accurately convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit to assess a patient's condition. A slight error in temperature reading could lead to misdiagnosis and inappropriate treatment.
In the field of climate science, temperature data is analyzed from all over the world, often reported in different scales. Scientists must convert this data to a common scale to compare and analyze trends. Accurate temperature conversions are crucial for understanding global warming, predicting future climate patterns, and developing strategies to mitigate climate change.
The conversion of 379 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit is not merely an academic exercise; it has real-world implications across various fields. The accuracy of these conversions is crucial for decision-making, safety, and understanding the world around us. By mastering the formulas and utilizing reliable conversion tools, we can bridge the gap between different temperature scales and gain a deeper understanding of the thermal environment.
Lets take a moment to explore how a simple temperature difference can affect a process. Imagine a chemical reaction that is optimized to occur at 714.2F (the Fahrenheit equivalent of 379C). If the temperature deviates by even a few degrees, the reaction rate, yield, or even the products themselves could be significantly altered. This is why precise temperature control and accurate conversions are so vital in chemistry and other scientific disciplines.
Moreover, consider the implications for material science. Many materials exhibit different properties at different temperatures. The strength, elasticity, and conductivity of a material can change drastically as it heats up or cools down. For example, 379C might be a critical temperature for a specific alloy used in aerospace engineering. Understanding the Fahrenheit equivalent (714.2F) is essential for designing components that can withstand extreme conditions.
The same principles apply to fields like electronics. Electronic components generate heat during operation, and excessive temperatures can lead to failure. Engineers need to carefully manage thermal conditions to ensure the reliability of electronic devices. Converting Celsius temperatures to Fahrenheit helps them assess the thermal load and design effective cooling systems.
Even in everyday life, temperature conversions play a role in our comfort and safety. When traveling to a country that uses Celsius, understanding how to convert temperatures to Fahrenheit is crucial for choosing appropriate clothing, adjusting to local weather conditions, and avoiding heatstroke or hypothermia.
For those who work in international business, understanding temperature conversions can facilitate communication and collaboration with colleagues from around the world. Whether its discussing product specifications, coordinating logistics, or planning events, accurate temperature conversions ensure that everyone is on the same page.
In conclusion, the ability to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit is a fundamental skill that transcends cultural and professional boundaries. It allows us to interpret data, make informed decisions, and communicate effectively in a world that uses different temperature scales. While online tools and converters can simplify the process, understanding the underlying formulas empowers us to critically assess the data and avoid potential errors. So, the next time you encounter a temperature in Celsius, remember the formula (c 9/5) + 32 = f, and unlock the meaning behind the numbers.
Consider the implications of 379C in the context of global warming and climate change. While this specific temperature might not represent a typical environmental condition, it underscores the importance of understanding temperature scales and their impact on our planet. As global temperatures rise, accurately converting and interpreting temperature data becomes increasingly critical for assessing the severity of the situation and developing effective mitigation strategies.
The ability to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit is not just about understanding numbers; it's about understanding the potential consequences of rising temperatures, melting glaciers, and extreme weather events. It's about making informed decisions to protect our planet and ensure a sustainable future for generations to come.


Detail Author:
- Name : Ansel Johnston IV
- Username : keebler.alek
- Email : bret88@gmail.com
- Birthdate : 1990-05-12
- Address : 71079 Kunze Avenue Apt. 627 North German, LA 74451
- Phone : +1.640.426.5747
- Company : Schiller, Dickens and O'Kon
- Job : Avionics Technician
- Bio : Aut est amet itaque voluptatem sed non. Cum provident praesentium omnis consectetur expedita illum commodi tempore. Aspernatur itaque nihil est. Minus cumque veniam et non enim exercitationem.
Socials
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/kshlerind
- username : kshlerind
- bio : A porro praesentium quia omnis facilis explicabo consectetur necessitatibus.
- followers : 5550
- following : 2985
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/derekkshlerin
- username : derekkshlerin
- bio : Et ad dolore non voluptatem. Laboriosam itaque tempora est omnis distinctio necessitatibus.
- followers : 2868
- following : 2319
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/derekkshlerin
- username : derekkshlerin
- bio : Ad et nesciunt nemo voluptas vero.
- followers : 6465
- following : 1911